In a 20 mins interview with Space Race, Richard Walker talks about our work on large earthquakes and active faults in Central Asia, tectonic geomorphology, our use of satellite data, DEMs, and much more.
Tag: fault
Our team has been working in the Tien Shan for many years now and we are very happy to present one of the key outcomes of our several projects. In the new book Earthquakes of Kyrgyzstan we provide an overview over strong earthquakes that occurred in Kyrgyzstan, both instrumental and from paleoseismological studies. The book is open access and can be downloaded here:
On 30 May, Ramon Arrowsmith from Arizona State University talked about Seismotectonics and surface rupture of large intraplate earthquakes: an example from the M7.8 1911 Kebin (Chon Kemin) Earthquake, Northern Tien Shan, Kyrgyzstan in the framework of our NATO-funded project SPS G5690 – “Earthquake Hazard and Environmental Security in Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan”. In case you missed Ramon’s presentation, here’s the video.
We’re going to have a summer break and commence our webinar series in autumn. Watch this space for future talks, which take place always on the last Monday of every month, and follow us on Twitter for updates: https://twitter.com/QuakesCentAsia.

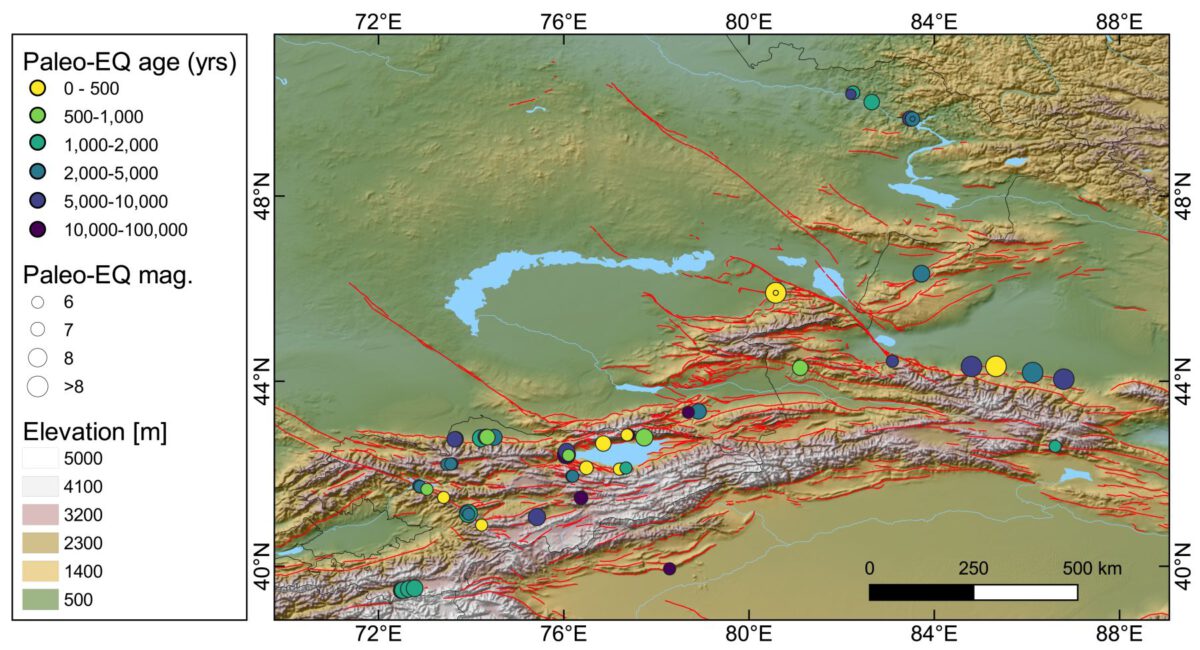
The Main Kopetdag fault (MKDF) of Turkmenistan is a key tectonic feature within the active tectonics of the Arabia-Eurasia continental collision and the geodynamics of the South Caspian basin. The fault runs along the edge of the Kopetdag (or Kopeh Dagh) mountains, which form the northern margin of the Arabia-Eurasia collision zone. The tectonics are complicated by proximity to the South Caspian Basin, which is an enigmatic ‘block’, filled with up to 20 km of Cenozoic sediment, and possibly floored by oceanic crust of Mesozoic age. The South Caspian is moving relative to its surroundings, with a roughly northwest motion relative to Eurasia that introduces oblique right-lateral and shortening components across the western Kopetdag. The lateral component decreases eastwards as the influence of the Caspian diminishes, and the Kopetdag instead accommodates Arabia-Eurasia shortening.

In the framework of our NATO-funded project SPS G5690 – “Earthquake Hazard and Environmental Security in Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan” we will run an ~1 hr online webinar. Ramon Arrowsmith from Arizona State University will talk about Seismotectonics and surface rupture of large intraplate earthquakes: an example from the M7.8 1911 Kebin (Chon Kemin) Earthquake, Northern Tien Shan, Kyrgyzstan.
The webinar is open for everyone interested and will be held via zoom (https://uni-jena-de.zoom.us/j/8941887790 Meeting-ID: 894 188 7790; Password: EQAsia).
Date: 30 May, 2022
Time: 3 pm UK time (3 pm London; 4 pm Berlin & Paris; 10 pm Beijing; 7 am San Francisco)
On 26 April, 2022, Jean-Francois Ritz from Géosciences Montpellier talked about Unprecedented surface rupture and shallow fault reactivation during the 2019 Mw 4.9 Le Teil earthquake, France: What does paleoseismology reveal? in the framework of our NATO-funded project SPS G5690 – “Earthquake Hazard and Environmental Security in Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan”. In case you missed Jeff’s presentation, here’s the video.
Watch this space for future talks, always on the last Monday of every month, and follow us on Twitter for updates: https://twitter.com/QuakesCentAsia

In the framework of our NATO-funded project SPS G5690 – “Earthquake Hazard and Environmental Security in Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan” we will run an ~1 hr online webinar. Jean-Francois Ritz from Géosciences Montpellier will talk about Unprecedented surface rupture and shallow fault reactivation during the 2019 Mw 4.9 Le Teil earthquake, France: What does paleoseismology reveal? The webinar is open for everyone interested and will be held via zoom (https://uni-jena-de.zoom.us/j/8941887790 Meeting-ID: 894 188 7790; Password: EQAsia).
Date: 26 April, 2022
Time: 3 pm UK time (3 pm London; 4 pm Berlin & Paris; 10 pm Beijing; 7 am San Francisco)

The South Caspian Basin (SCB) is an aseismic block that moves independently to its surroundings. Together with the Arabia-Eurasia collision, it controls the active tectonics of Turkmenistan. The directions, rates, and rotation poles of the SCB relative to Iran and Eurasia are not well resolved. In a new paper recently published in TECTONICS, we constrain the motion of the SCB by measuring the slip rate of the Main Kopeh Dagh Fault (MKDF) in Turkmenistan. Here’s what we found:

In November 2021 two of us (Ian Pierce and Richard Walker) were able to travel to Baku to begin a collaborative project between the Azerbaijan National Academy of Sciences and the University of Oxford addressing regional tectonics, active faulting, and earthquake hazard. The project was due to begin in early 2020 but was postponed due to travel restrictions.
On 25 October, 2021, Richard Walker from the University of Oxford gave the fourth talk of our lecture series on the tectonics of Central Asia. The topic was “Active Faulting, earthquakes, and geomorphology of the Main Kopeh Dagh Fault, Turkmenistan. The talk was presented on 2021-10-25.” . In case you missed Richard’s presentation, here’s the video.
Watch this space for future talks, always on the last Monday of every second month, and follow us on Twitter for updates: https://twitter.com/QuakesCentAsia